Welcome to On Verticality. This blog explores the innate human need to escape the surface of the earth, and our struggles to do so throughout history. If you’re new here, a good place to start is the Theory of Verticality section or the Introduction to Verticality. If you want to receive updates on what’s new with the blog, you can use the Subscribe page to sign up. Thanks for visiting!
Click to filter posts by the three main subjects for the blog : Architecture, Flight and Mountains.
Zoning Envelopes and the New York Skyscraper
Back in architecture school, I had a professor once say that the most effective way to create change is to adjust the building code. That way every architect must conform their designs to meet the code’s requirements, which is much more impactful than any single building could ever be. It was sage advice, and throughout the history of skyscrapers, it rings true. Throughout the history of skyscrapers, arguably the most influential of these changes occurred in 1916 in New York City.
By the size of the work, we measure the size of man
The above illustration is from the cover of an 1889 issue of Le Central. It shows a caricature of Gustave Eiffel standing in between his Eiffel Tower and the Great Pyramid. Inscribed on the pyramid is the phrase A la grandeur de l'oeuvre on mesure la grandeur de l'homme, or By the size of the work we measure the size of man. It’s a statement on verticality, and it illustrates how the height of these structures is their defining characteristic in the eyes of the public.
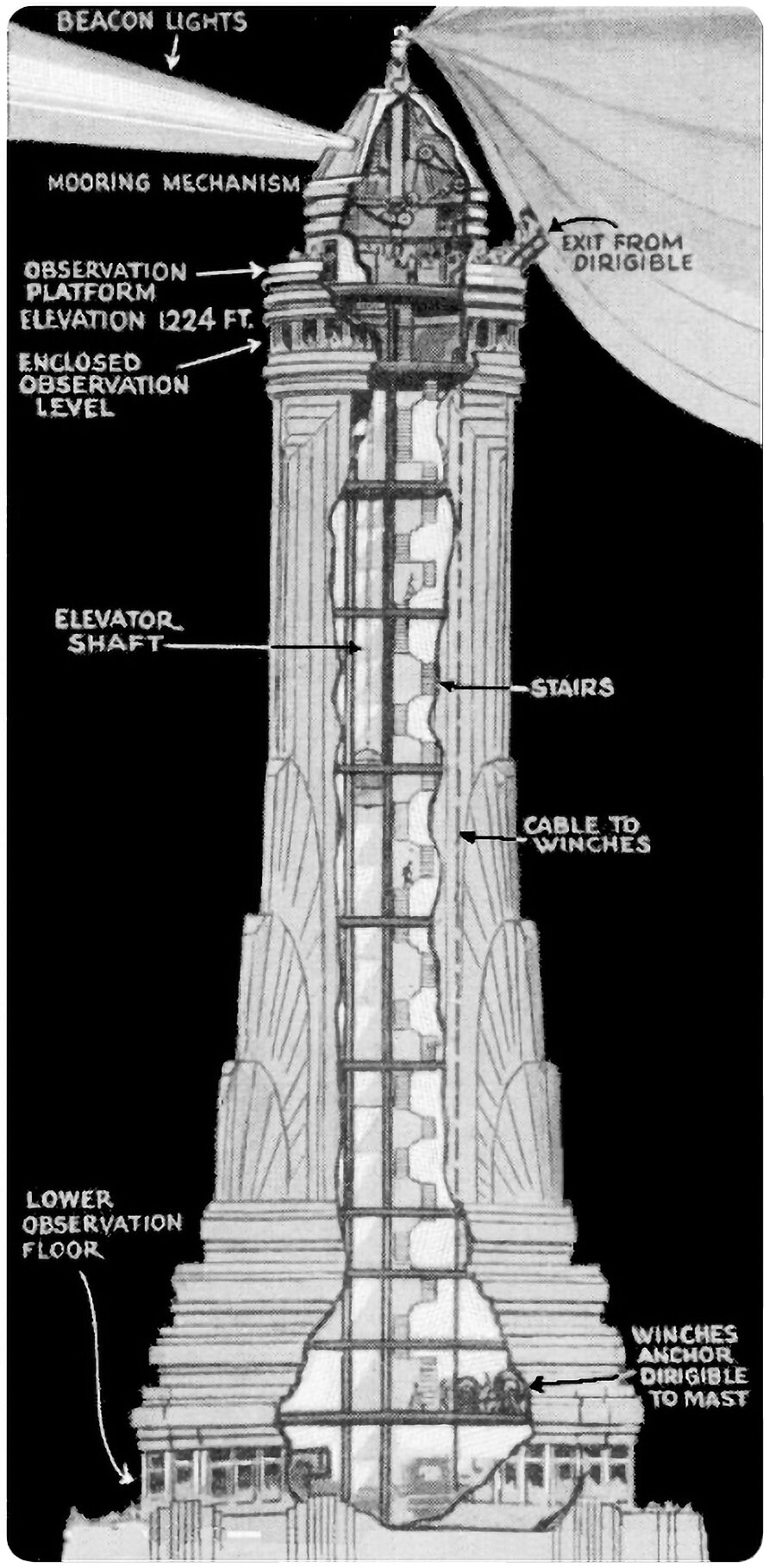
The Empire State Building’s Mooring Mast
Pictured above is an illustration from Popular Mechanics that shows the Empire State Building’s proposed mooring mast. This mast was designed to act as a dock for dirigibles, who could moor themselves to the top of the tower’s crown and load and unload passengers. It’s a wild idea, albeit completely impractical.
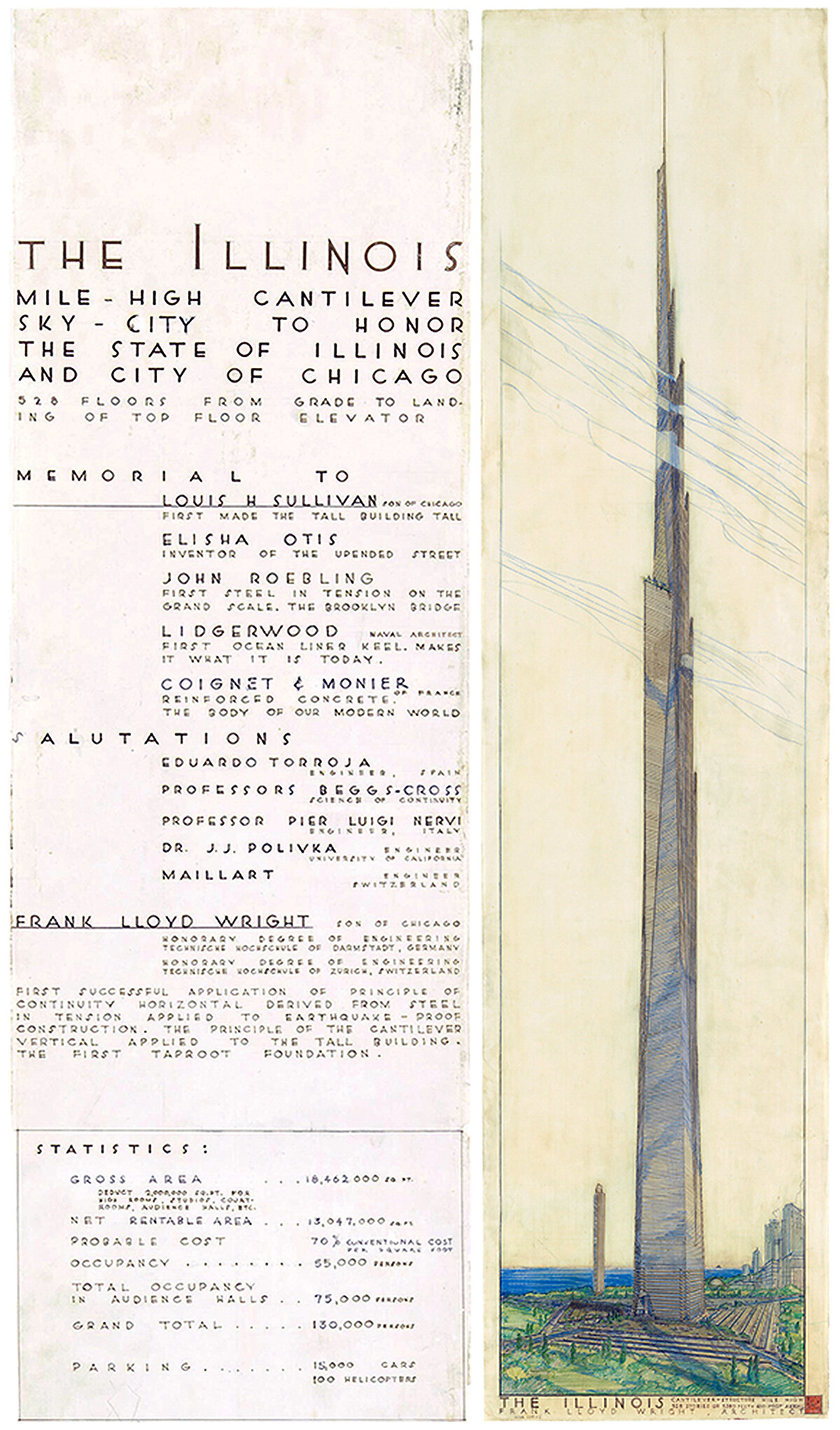
Frank Lloyd Wright’s Mile High Skyscraper Proposal
Frank Lloyd Wright was an outspoken advocate for low-density cities without skyscrapers. With this in mind, it’s hard to believe the tower design pictured above came from Wright. It’s called The Illinois, and it was planned to be a mile (1,609 meters, or 5,280 feet) in height. That’s more than four times the height of the Empire State Building, and nearly twice the height of the Burj Dubai.
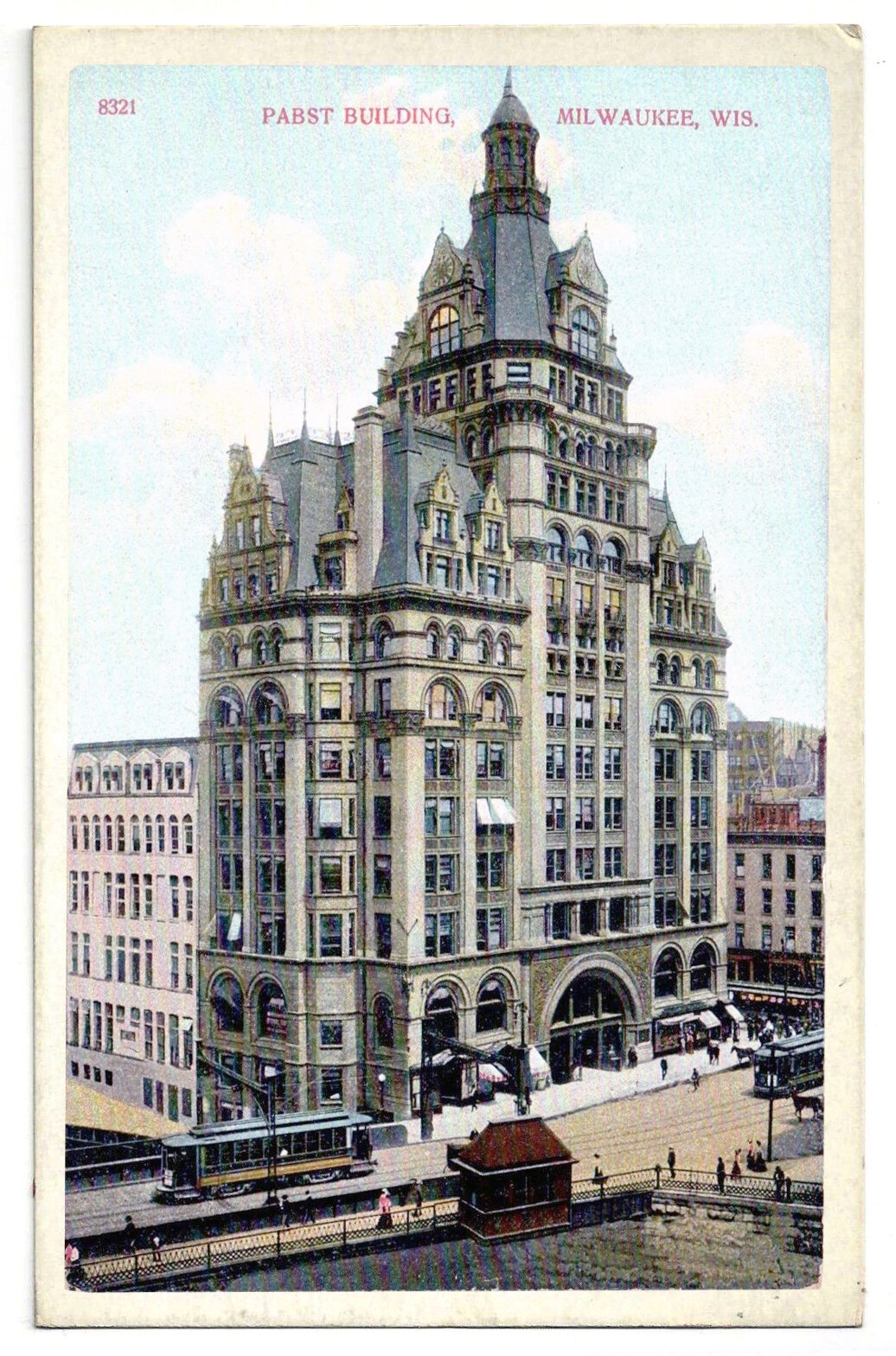
The Pabst Building and the Symbolism of Verticality
In 1890, Frederick Pabst purchased a plot of land at the center of downtown Milwaukee, on which he planned to build a headquarters for his brewing empire. A year later, the Pabst Building was complete. Standing fourteen stories and 235 feet (71 meters) tall, it was the tallest building in the city at the time, and it was a wonderfully detailed example of the Renaissance Revival style. Being Milwaukee’s tallest building was symbolic for Pabst and for the city, however his building’s dominance wouldn’t last as long as he’d hoped.
Alternate Realities : The Great Tower for London Competition
In 1890, an open competition was held to design the Great Tower for London in the soon-to-be-opened Wembley Park. The tower was to be the tallest in the world, and it would claim the title from the Eiffel Tower in Paris, completed the year before. An open competition was held, which received 68 submissions from all over the world. Together, these designs provide a rich cross-section of the world’s architectural taste at the time.
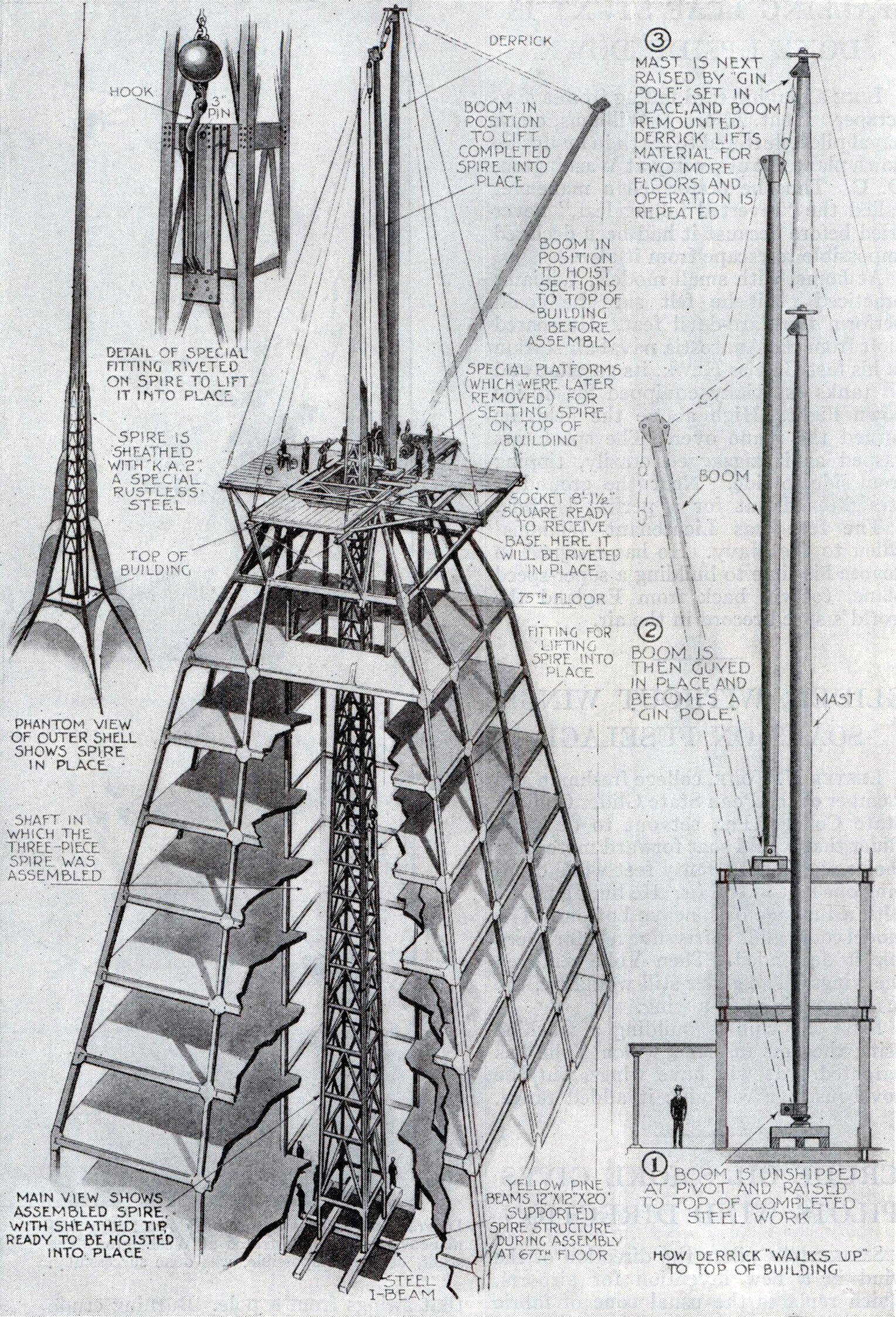
The Chrysler Building’s Hidden Spire
If you’re competing to build the tallest building in the world, and you want to conceal the final height until the last possible moment, how do you go about it? Well, you construct the spire inside the crown of the building, wait for your competitor to finish his tower, then lift your spire into place and take the title from him, of course.
Alternate Realities : The Eiffel Tower
There’s an interesting subtext to unbuilt projects throughout the history of architecture. Unbuilt additions to existing buildings are the most intriguing, because they respond to an existing mind-scape rather than create a new one. The above illustration is a perfect example of this. It shows a preliminary design for the Eiffel Tower in Paris, drawn by French architect Stephen Sauvestre.
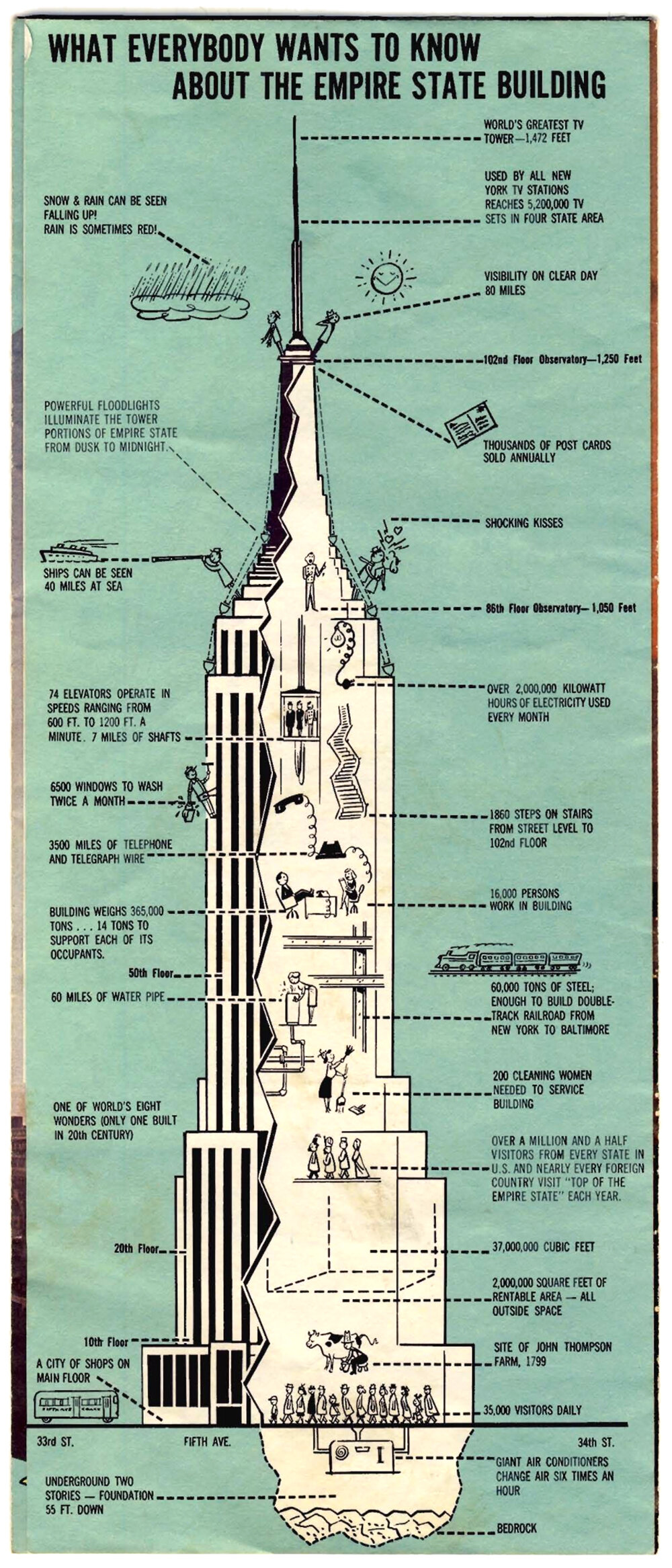
What Everybody Wants To Know About The Empire State Building
Only the most famous and iconic buildings of the world get their own marketing. The Empire State Building in New York City is one of these, and the brochure pictured above is a fantastic little bit of marketing for the tower. I don’t know when it was made or where it was sold, but given the television antenna at the summit, which was installed in 1965, it’s probably from the late 1960’s or 70’s.
“As its basic fact and most critical element, it is structure that is at the heart of the tall building’s design.”
-Ada Louise Huxtable, American architecture critic, 1921-2013
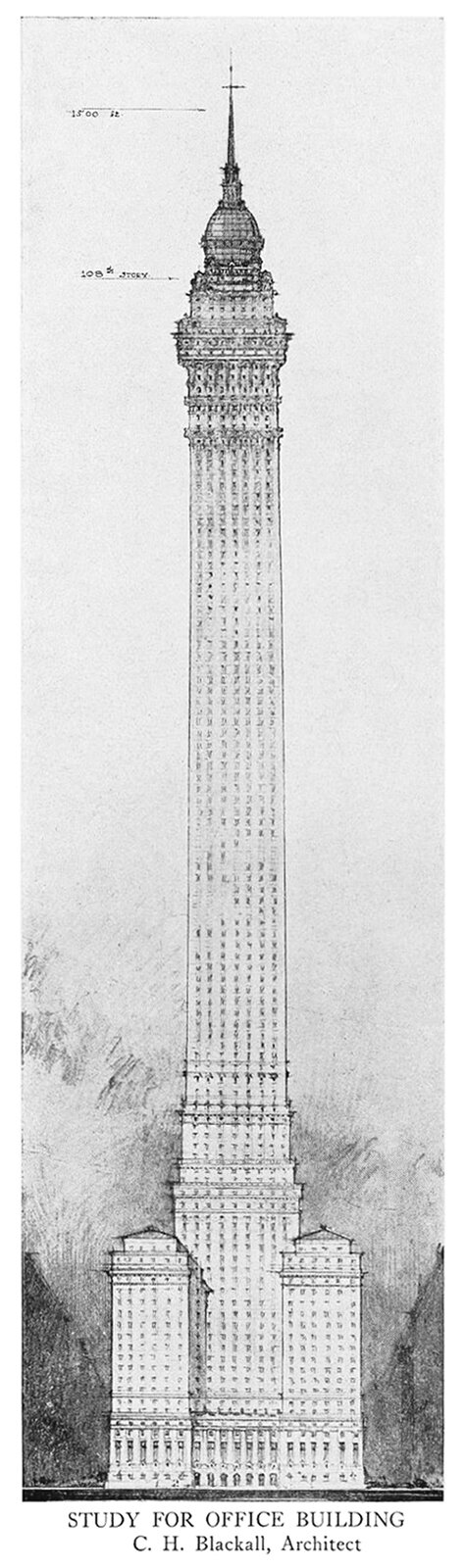
Clarence H. Blackall’s Study for an Office Building
The above illustration originally appeared in an exhibition for the Boston Architectural Club in 1912. The subsequently published yearbook containing the drawing gives no context or background, just the cryptic title Study for Office Building and the architect’s name, Clarence H. Blackall.
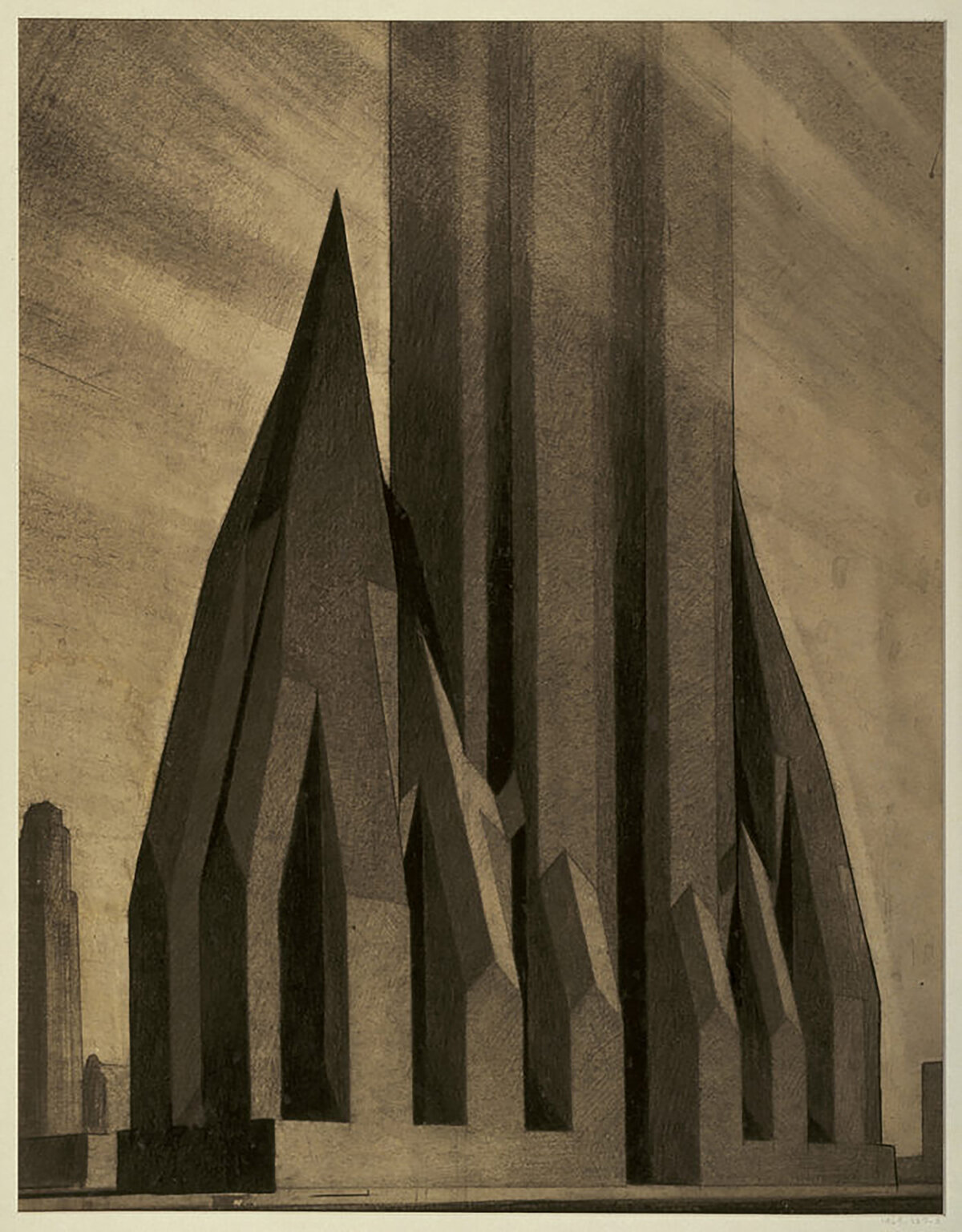
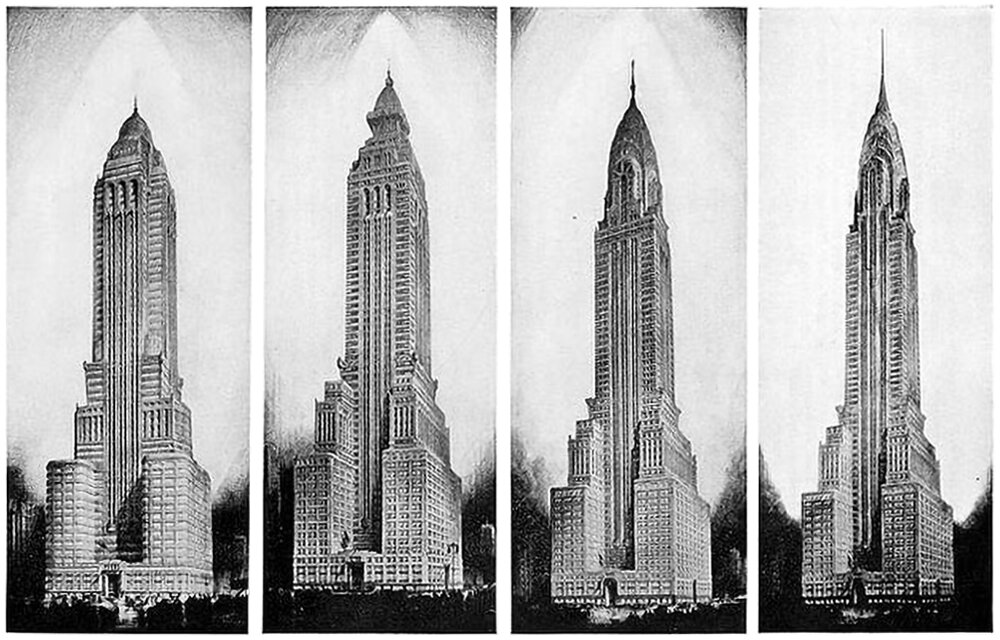
Alternate Realities : The Chrysler Building
The design process is never-ending. The only reason there’s an end is because something needs to get built, and it usually needs to happen quickly. It’s like a film, and the built result is like a snapshot from somewhere near the end of the film. .e image for example, showing. The above illustration is a good example. It four proposed designs for the Chrysler Building in New York.
“The skyscraper is Orwellian or Olympian, depending on how you look at it.”
-Ada Louise Huxtable, American architecture critic, 1921-2013.
Alberto de Palacio’s Monument to Christopher Columbus
The phenomenal success of the Eiffel Tower has impressed upon the projectors of coming exhibitions the idea that they must strive to rival (if not to surpass) that unique structure by some colossal monumental work. This is the first sentence of an article from 1891 announcing the proposal pictured above. It was a monument to Christopher Columbus, and it was designed by Spanish engineer Alberto de Palacio, to be built for the 1893 World’s Fair in Chicago.
A Design for Converting The Crystal Palace Into A Tower 1000 Feet High
Most people familiar with the history of modern architecture know the Crystal Palace. It was built in Hyde Park, London for the Great Exhibition of 1851, and it was designed by Joseph Paxton. What most people don’t know, however, is another architect took the pieces of the Crystal Palace and re-arranged them into a supertall tower proposal. It wasn’t built, of course, but it’s a fascinating proposal that takes advantage of the temporary nature of the original building.
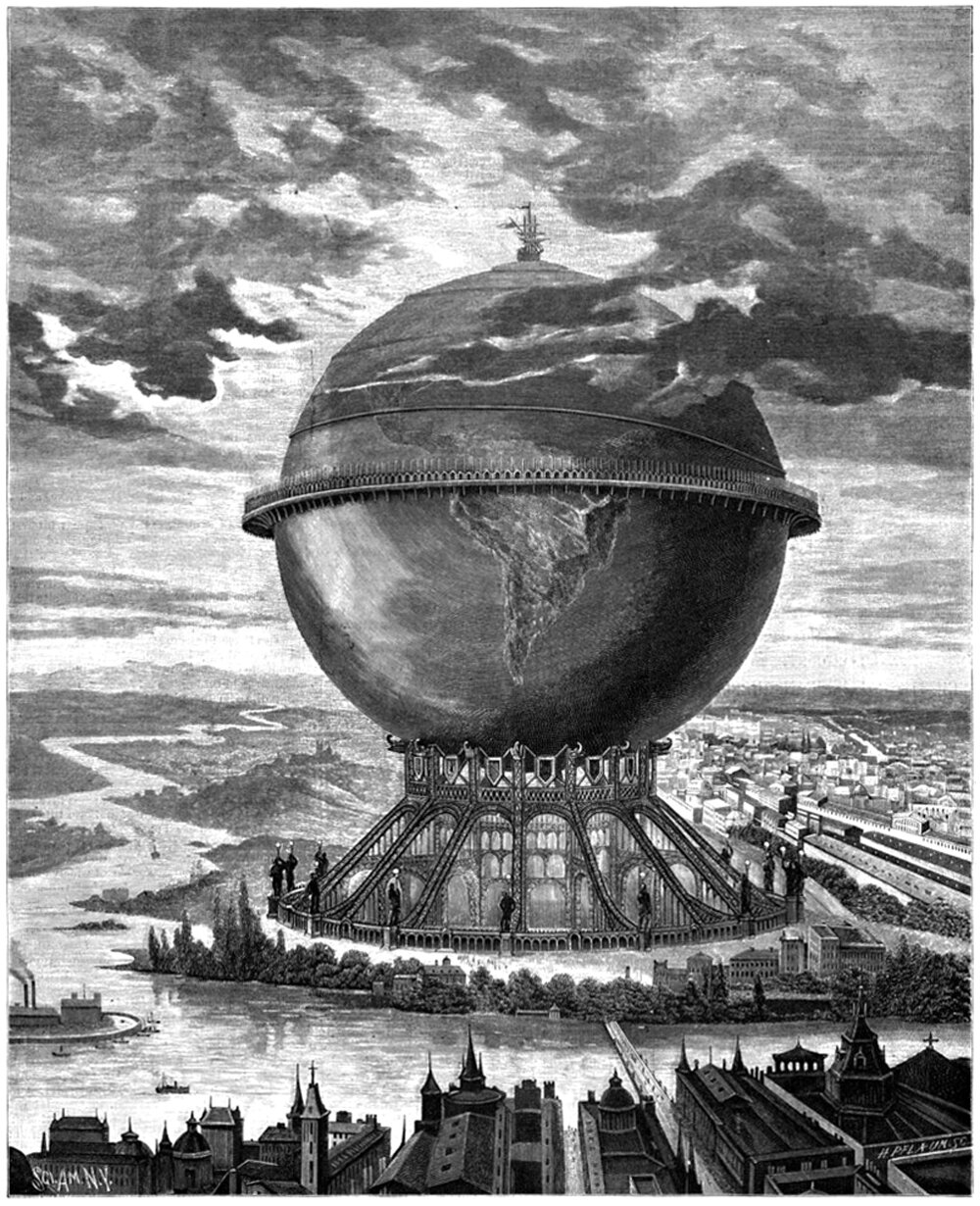
The Coney Island Globe Tower
Pictured above is the Coney Island Globe Tower, proposed in 1906 by Samuel Friede for a lot at the corner of Steeplechase Park in Coney Island, Brooklyn. The building features an enormous globe built of latticed steel, similar in style to the Eiffel Tower. The Globe was designed as an entertainment and leisure complex, and it was marketed as the second tallest building in the world, behind the aforementioned Eiffel Tower. The most intriguing part of the proposal, however, is that it was a fraud.
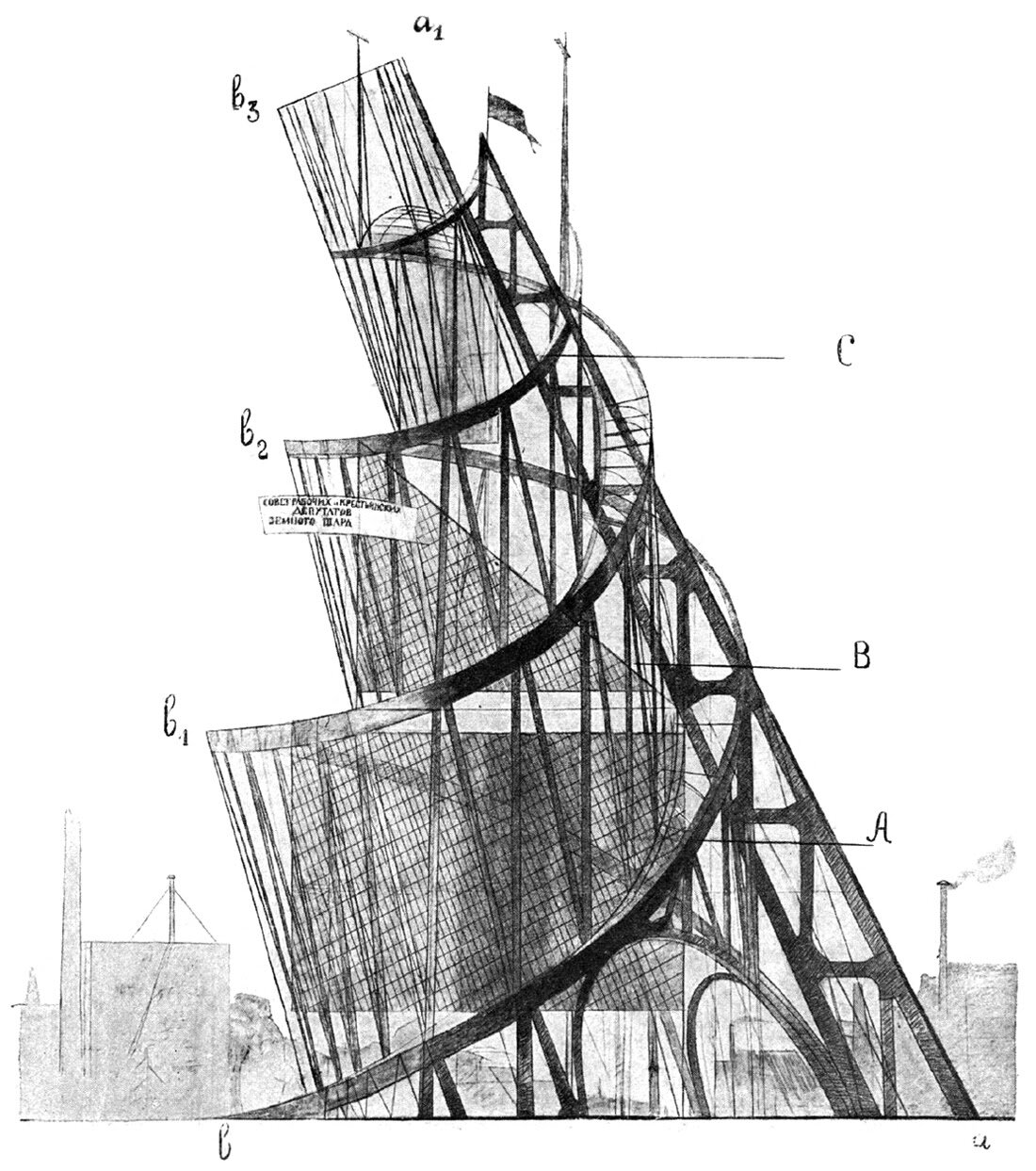
Vladimir Tatlin’s Tower
Tatlin’s Tower has always made me uneasy. There’s something about it’s form that rubs me the wrong way, but at the same time, it’s strangely captivating. In school, I was exposed to it many times in architecture history classes, but it was always glossed over as just another example of Russian Constructivism. Let’s take a closer look and see just how strange it is.
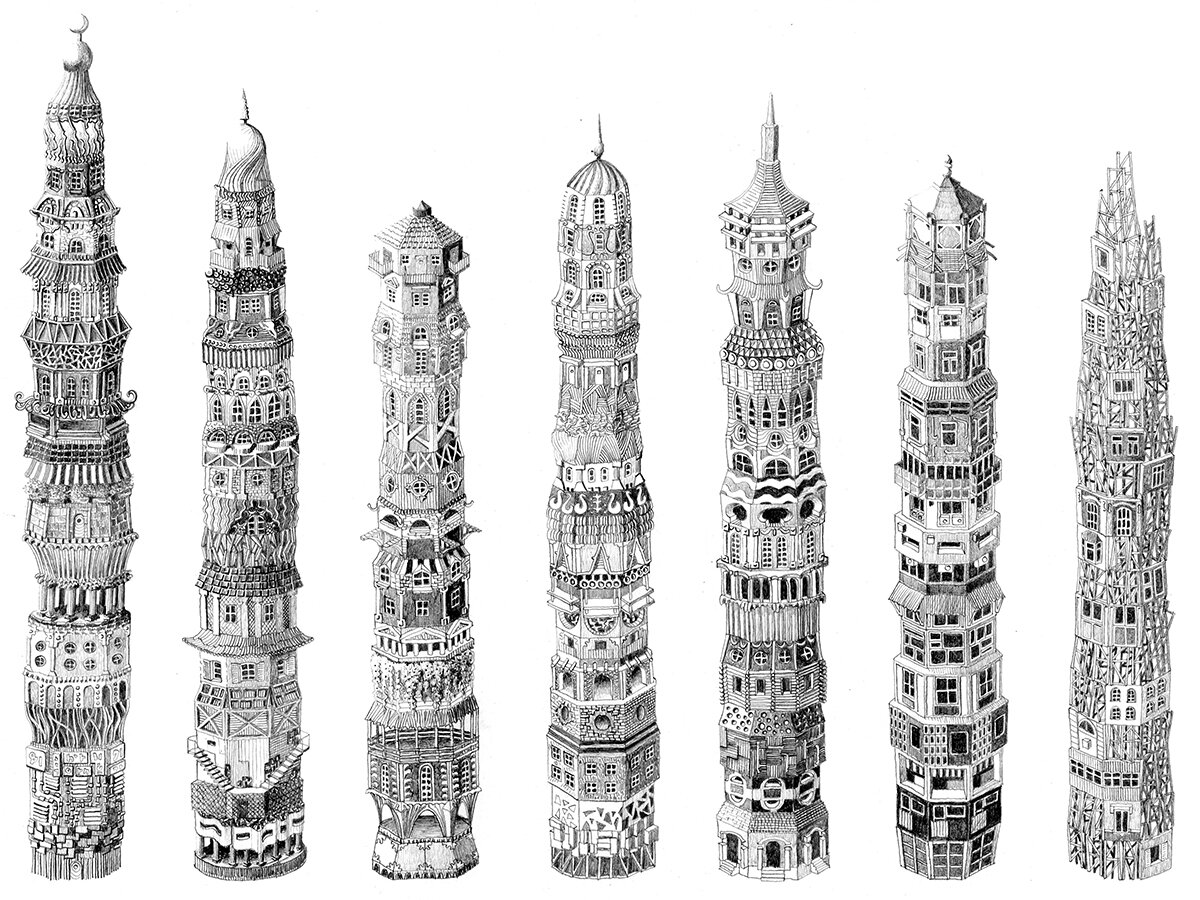
Stacking Typologies
When designing a skyscraper, an architect usually takes a holistic approach. This means the entire building is designed with a common strategy, which usually translates into a single aesthetic. In short, each building has a style. What happens when you start mixing styles together? At the surface, this would sound like blasphemy to most architects practicing today, but let’s ponder it.
“A skyscraper is the incarnate rebellion against the supposedly unattainable; against the mystery of altitude, against the otherworldliness of the cerulean.”
-Joseph Roth, Austrian journalist and novelist, 1894-1939
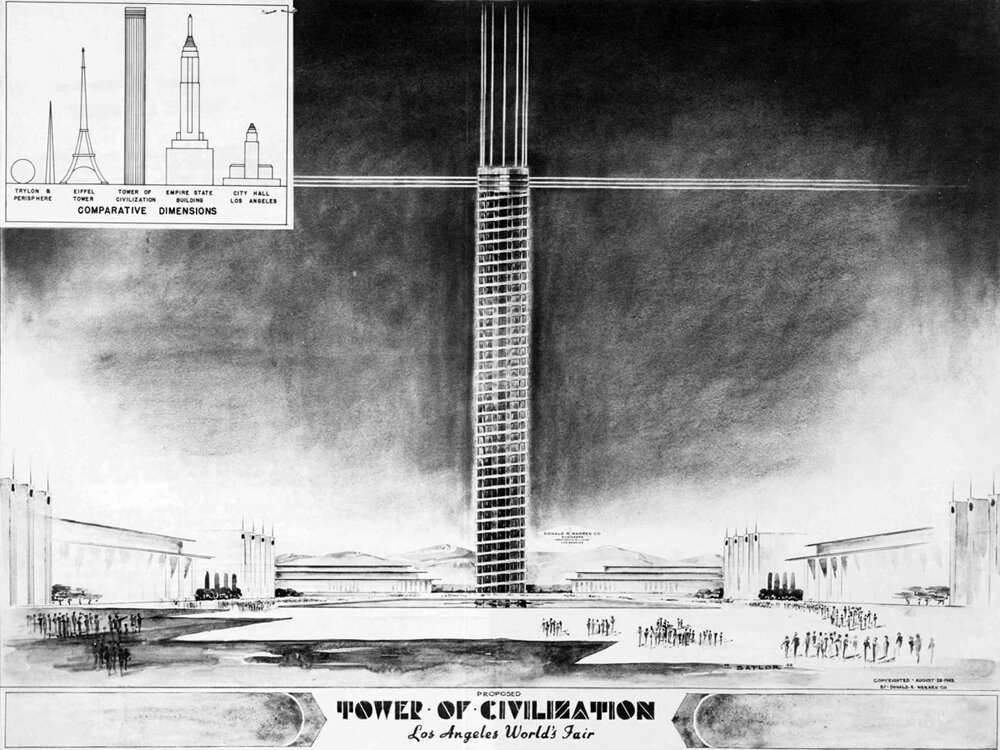
The Tower of Civilization
This is the proposed Tower of Civilization, designed by civil engineer Donald R. Warren for the planned, but never held, 1939 World’s Fair in Los Angeles. It would’ve been the centerpiece of the event and the tallest building in the world, coming in at 393 meters, or 1,290 feet tall. The tower was no doubt meant to signify the status of Los Angeles as a world-class city, and it used Verticality to do so.