Welcome to On Verticality. This blog explores the innate human need to escape the surface of the earth, and our struggles to do so throughout history. If you’re new here, a good place to start is the Theory of Verticality section or the Introduction to Verticality. If you want to receive updates on what’s new with the blog, you can use the Subscribe page to sign up. Thanks for visiting!
Click to filter posts by the three main subjects for the blog : Architecture, Flight and Mountains.
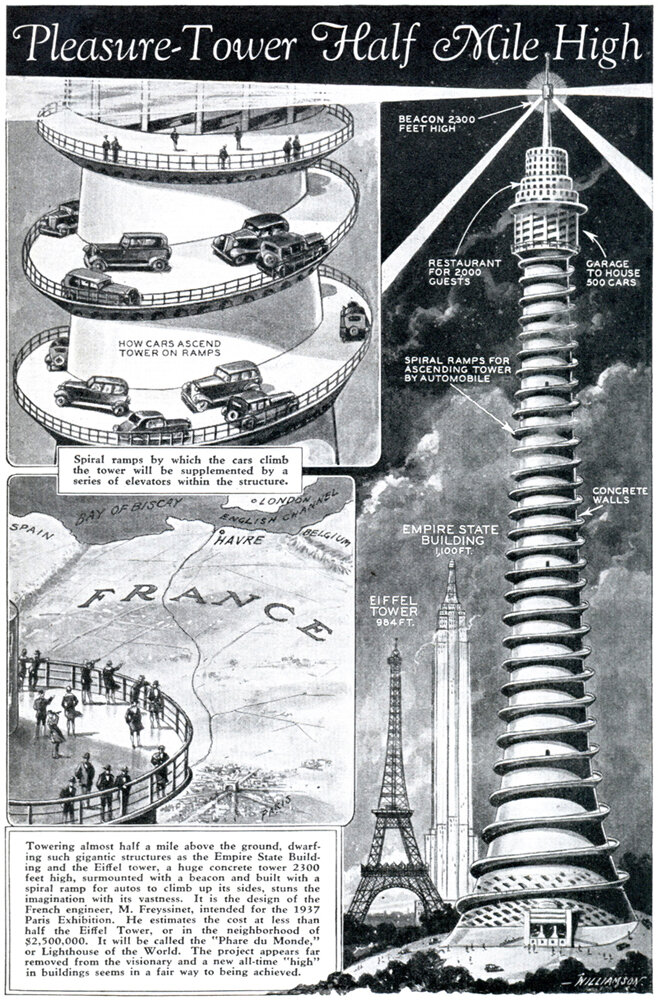
The Phare du Monde Pleasure Tower
Pictured above is a tower proposal from 1933 for the 1937 World’s Fair in Paris. It features an external spiral ramp leading to a parking garage 1640 feet (500 meters) from ground level.[2] Once at the top, visitors would find a restaurant, hotel and observation deck, and the spire contained a lighthouse beacon and a meteorological cabin. The view? Sublime. The design? Utterly ridiculous, unless taken as a satirical statement on civilization’s reliance on the automobile.
Hugh Ferriss and Religion on the Skyline
Hugh Ferriss was an architect and illustrator, best known for his charcoal renderings of skyscrapers in the first half of the 20th century. Pictured here is an illustration from his 1929 work The Metropolis of Tomorrow, titled Religion. This image and the underlying thought behind it’s creation ties into a larger trend around this time that saw religious structures attempt to re-take the skyline from commerce.
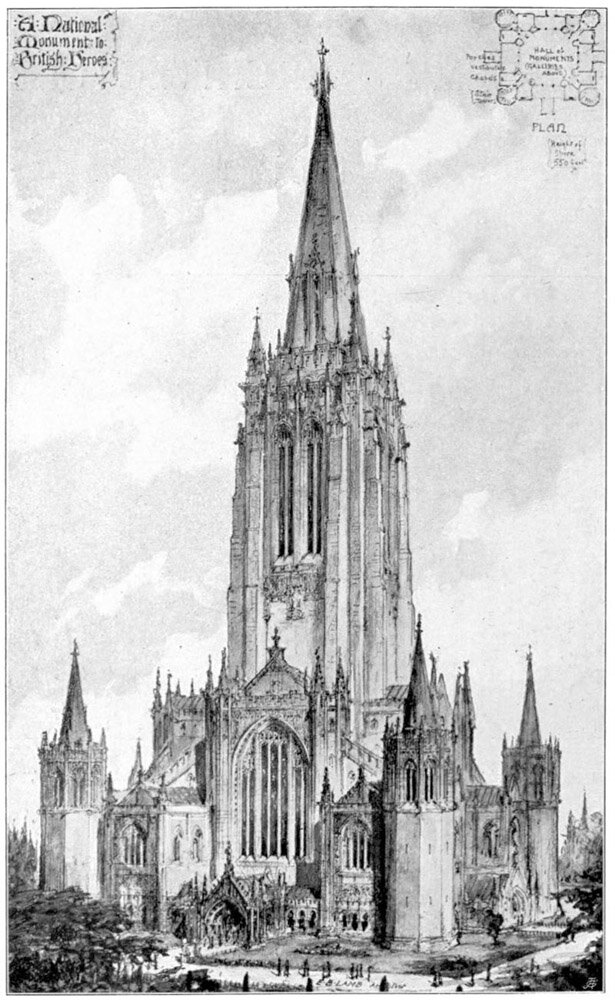
Edward B. Lamb's Monument to British Heroes
This is the National Monument to British Heroes, proposed by Edward B. Lamb in 1901. The structure was meant to house a hall of monuments and galleries, presumably to honor those who had died for the British crown throughout history. The proposal consists of a massive central belfry topped with a steeple and flanked by four turrets at its base.
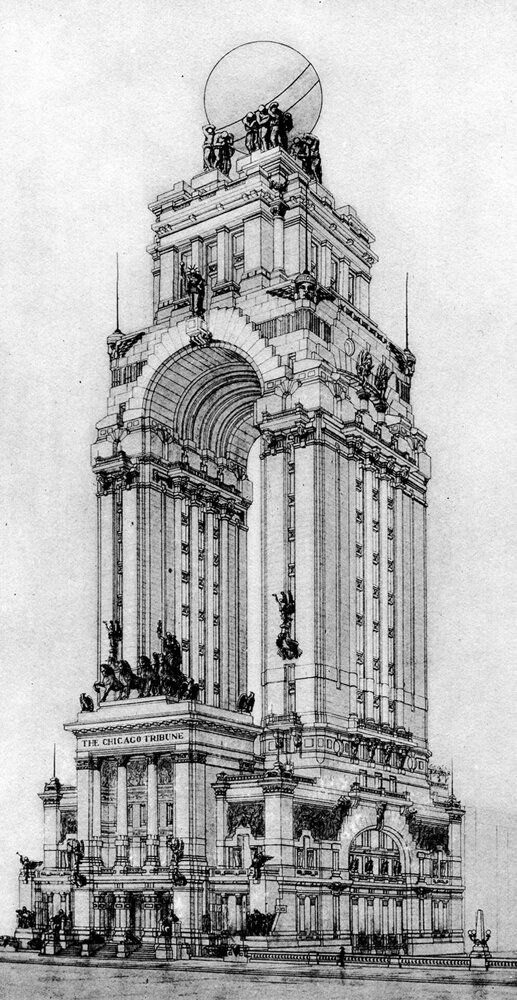
Saverio Dioguardi's Tribune Tower Proposal
Every time I research the Chicago Tribune Tower competition, I run into this proposal by Italian architect Saverio Dioguardi. His design is wonderfully flamboyant, and it’s more of a monument than a building. There’s something eye-catching about the sheer audacity of it, however, which is why I’ve singled it out here.
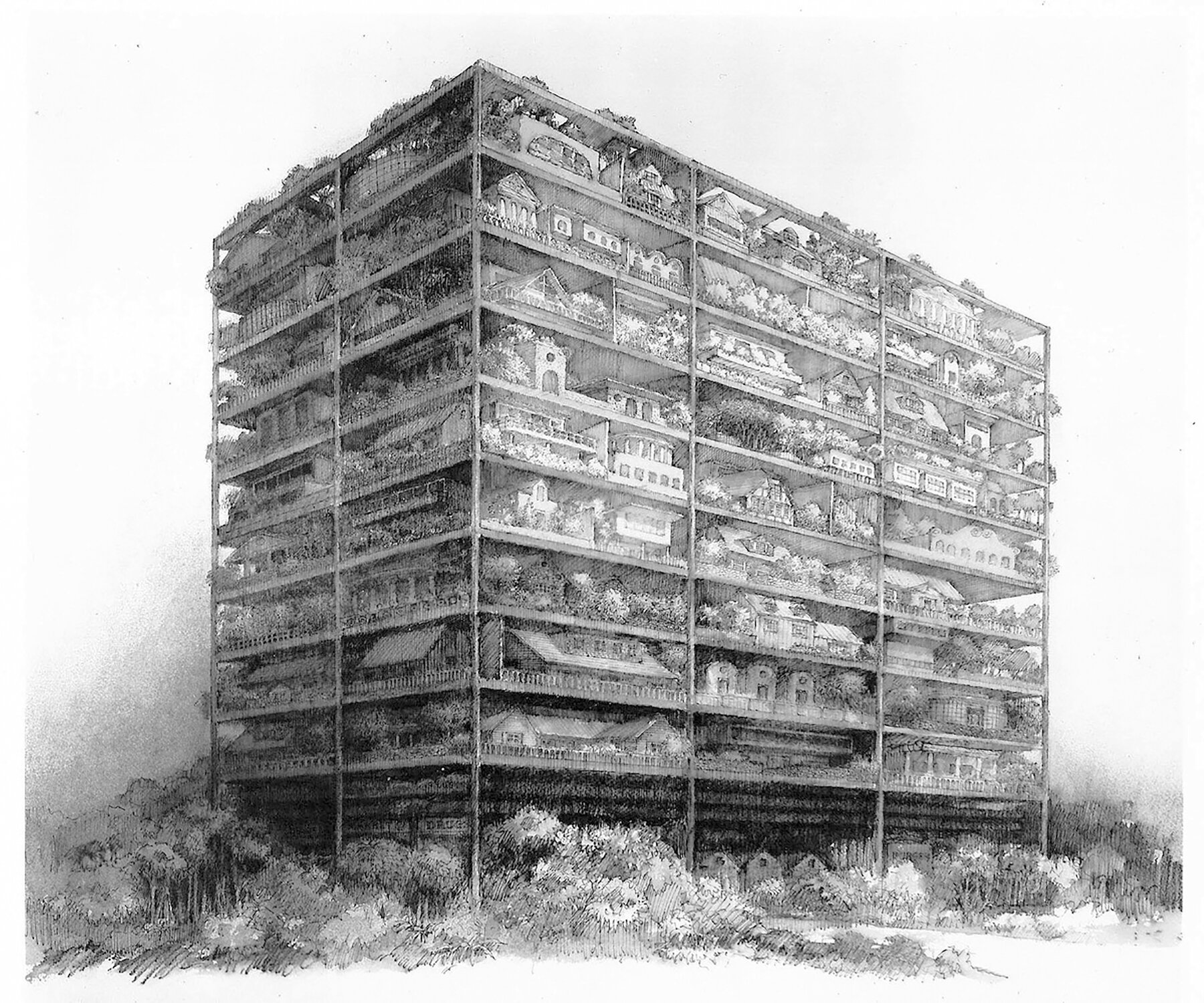
James Wines and the Highrise of Homes
This is the Highrise of Homes, designed in 1981 by James Wines and his firm SITE. The project consists of a series of stacked levels with individual homes built throughout each level. These homes appear much like the single-family detached homes of suburbia, which is a curious mashup of typologies. Wines is using Verticality to re-arrange a typical suburb into a vertical tower, complete with sidewalks, front and back yards, and pitched roofs. This rearrangement creates some curious scenarios and experiences which are worth pondering.
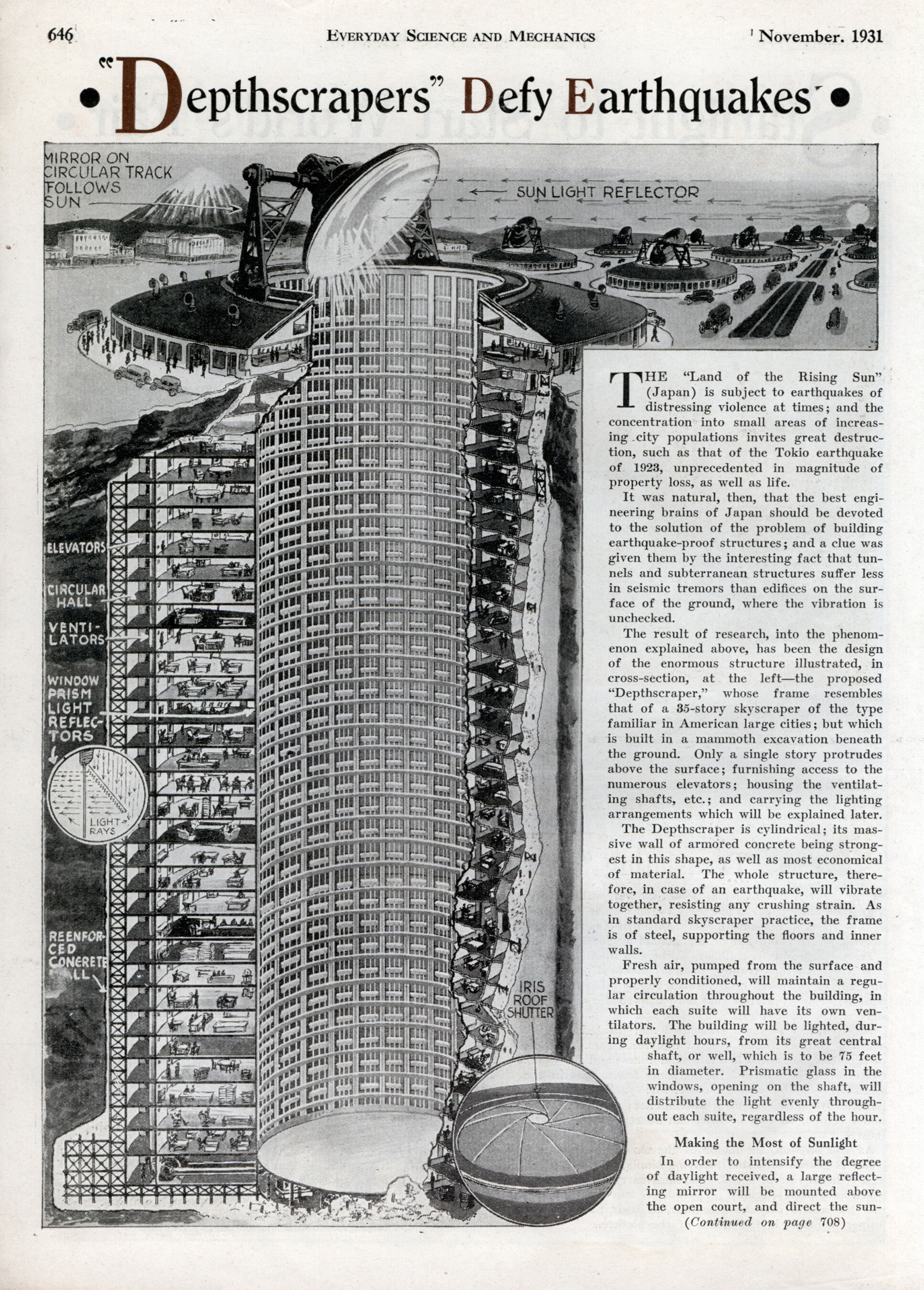
The Earthquake-proof Depthscraper
Take a look at this design for a subterranean tower from Everyday Science and Mechanics in 1931. The structure was designed by Japanese engineers in response to earthquake concerns, so the building claims to be ‘earthquake-proof’. Technical aspects aside, questions abound regarding the experience of living or working in such a structure.
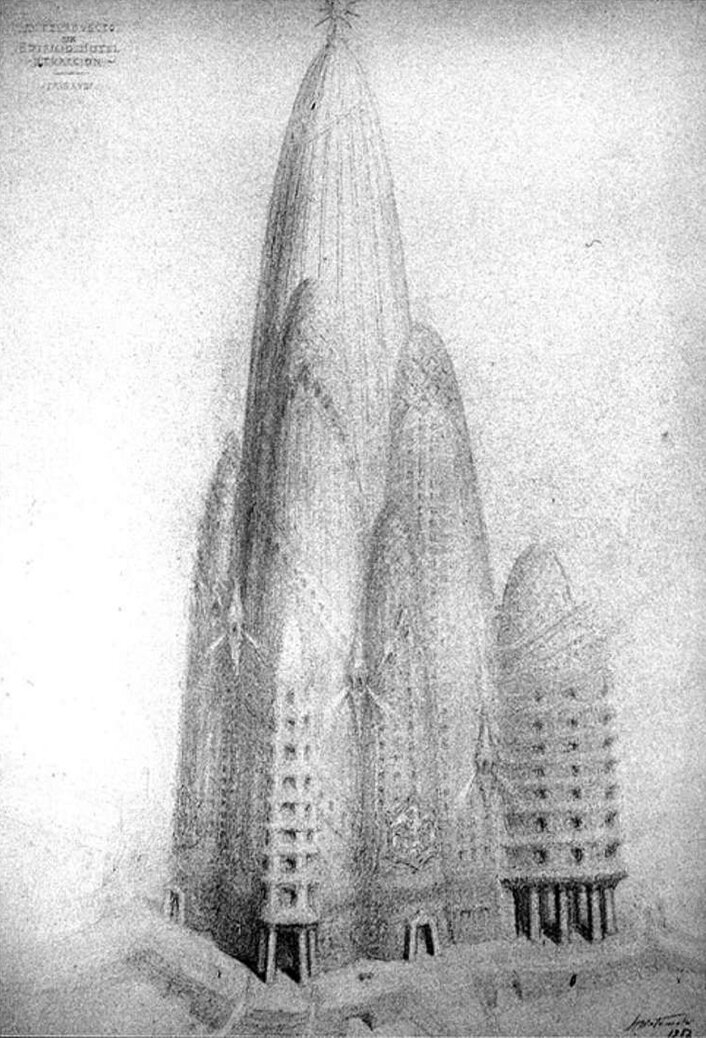
Antoni Gaudí's New York Skyscraper
The Spanish architect Antoni Gaudí is known the world over for his iconic architecture, rich in organic, curvilinear forms. One lesser-known project of his is the Hotel Attraction. It was designed in 1908 for an unspecified site in Lower Manhattan, New York City. The project would have housed a hotel, restaurants, theatre hall, exhibition hall, galleries, and a panoramic lookout at the top, called the 'Space Tower'. If built, it would have been 360 meters, or 1,181 feet tall.